Git - More Secure Commit
2019, 21 AprilHi, so I was exploring about git signing and it’s benefit.
If you have used git, you must have known that it is a distributed version control system. Every copy of a git repo (including local one) contains the whole information of the repository.
Git service provider such as Github, Gitlab and Bitbucket provides authentication by using each account credentials. Each has the capability to verify who pushed the commit to remote endpoint. This feature isn’t part of the git feature. If we try to check locally, we can’t know who pushed the commit.
There are basic information provided in git commit to try to identify who is doing the commit. But the information can’t be trusted and verified because it can be set by anyone using any value.
For example, with these command, I can set the commit information using John Doe’s name and email:
git config user.name John Doe
git config user.email john.doe@dronjax.com
So, how do we identify who actually does the commit? That’s what git signing feature is for.
One way to sign git commits is to use GPG, it’s an implementation of OpenPGP.
Note: It may look like GPG and OpenPGP spelling is similar, but they are different. One is implementation while the other is protocol.
Setup and Key Generation
First, you need to install GPG binary to your local machine.
After that, you need to generate a new key by running this command:
gpg --generate-key
You will be prompted for your informations (Name and Email). For starter, you can fill your primary email. We will get to the part where you can add other emails.
You will also be prompted to enter passphrase. It is best that you fill it up to secure your key in case it is stolen.
After that, there will be message like these:
gpg: key JOHNDOEKEYID marked as ultimately trusted
Note that JOHNDOEKEYID is the id of the GPG key.
Associate more emails
If you don’t need to add more emails (example: company email), you can skip to Enable Git Signing.
Nowadays, it’s normal that people have multiple emails. Most people probably have 2 or 3 of them. One of them is bound to be company email which is assigned to them.
Let’s assume you use github for hosting company repository. There is a chance that you use your personal account but link the company email. When you want create a commit, you may need to use company email to mark the commit.
For the case above, you don’t need to create a separate GPG key to sign the git commit. One GPG key can be associated with more than one email.
Now, the part where we associate new email starts with:
gpg --edit-key JOHNDOEKEYID
An interactive GPG shell will show up, you can list the command available by using help. In this post, we just gonna associate a new email by:
gpg> adduid
Similar to the early part, you need to specify name and email (you can add comment too). After you enter the information, you will be prompted for key password.
After adding the user, don’t forget to run:
gpg> save
If you don’t run the command above, any changes won’t be persisted in the GPG key.
Enable Git Signing
Now, we get to the main part to sign the git commit. For signing the git commit, we just need to change the git config by running the following command:
git config user.signingkey JOHNDOEKEYID
After setting up the key to sign in git, you can just sign your commit everytime by adding -S parameter. Example:
git commit -S -m "Some wonderful message."
Or alternatively, you can ensure that every commit always signed by running:
git config commit.gpgSign true
Verifying Git Signature
Now now, signing git commit is nice and all, but how do we verify the signed commit.
You can see the signature of the commit in git log by running:
git log --show-signature
You will need to know the public key of the person to fully verify the commit.
Alternatively, some git service provider provide a way to upload the public key signature. For example, in github the keys can be added from this link.
To show the public GPG key, you can run the following command:
gpg --export --armor JOHNDOEKEYID
The result of the command above, can be uploaded to git service provider or shared between coworkers for verification.
If you are using github, then you can see nice sign of verified like the following screenshot:
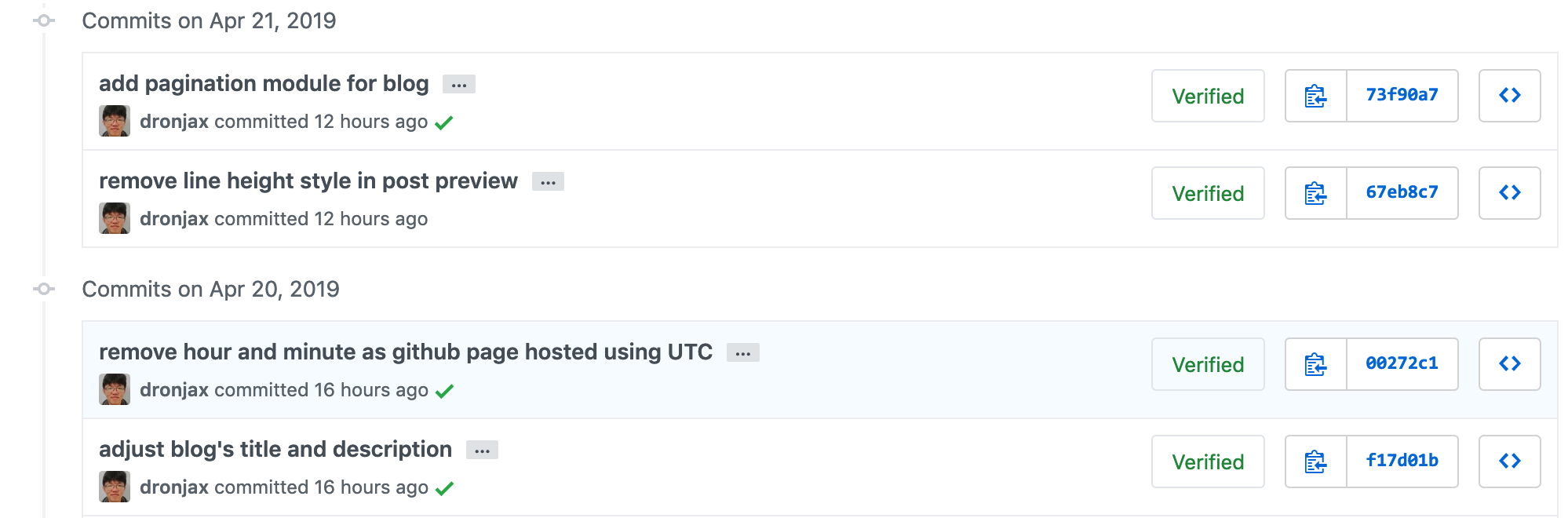
Or you can also see it yourself at this link.
Summary
By default, if we use git basic feature, it is possible for someone to impersonate John Doe by changing git author name and email.
Now, since John Doe enable git signing on all his commits and share it with his colleagues, all his colleagues can verify his commits.
John Doe has successfully protected himself from impersonation from anyone.
You should start protecting yourself too.